EU Cybersecurity laws for Medical devices are advancing, and the use of software medical devices is also increasing daily. The increased interconnection of medical devices to computer networks and technological convergence have made devices and software programmes vulnerable to mishaps.
The importance of protecting patient data from cyber-attacks is now well recognised. With the advancement of software as a medical device, proper regulations must be established to ensure the safety and security of medical devices.
Read our article on SaMD regulations in the EU and UK to understand software medical devices. This article discusses the cybersecurity aspects of medical devices.
Why is cybersecurity important for medical devices?
Medical devices contain crucial patient information. Healthcare data has been the most common target for data breaches for over a decade. These data breaches contribute to the data leak; even patient life can be in danger due to outdated software.
Ready to Streamline Your Regulatory Compliance?
Join hundreds of companies who trust OMC Medical for their regulatory needs. Get expert guidance and ensure compliance across all markets.
Call Now +44 208 066 7260EU Cybersecurity Laws for medical devices
Within the EU, the following legislative acts apply concurrently to the Medical Devices Regulations. These are important to the cybersecurity of medical devices or operators dealing with the protection or processing of personal data held in medical devices:
- NIS Directive or Directive 2016/1148 of the European Parliament and of the Council of 6 July 2016 concerning measures for a high common level of security of network and information systems across the Union
- GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or Regulation (EU) 2016/679 of the European Parliament and the Council on the protection of natural persons regarding the processing of personal data and the free movement of such data
- EU Cybersecurity Regulation or Regulation (EU) 2019/881 of the European Parliament and the Council on ENISA (the European Union Agency for Cybersecurity) and information and communications technology cybersecurity certification and repealing Regulation (EU) No 526/2013 (Cybersecurity Act)
NIS Directive or Directive 2016/1148 aims to achieve cybersecurity in the EU by ensuring the following aspects:
- Increase the preparedness of Member states by requiring them to be appropriately equipped
- Setting up a cooperation group, there is cooperation among the Member States. This includes setting up of a Computer Security Incident Response Team (CSIRT) and a competent national NIS authority
- A custom of security in all vital economic sectors like banking, energy, transport, etc
GDPR (General Data Protection Regulation) or Regulation (EU) 2016/679 governs the processing of personal data belonging to individuals in the EU. Personal data is any information used to identify or find a living person. Many parts of information that, when gathered, can lead to the identification of a specific person constitute personal information.
EU Cybersecurity Regulation or Regulation (EU) 2019/881 establishes European Cybersecurity Certification Framework for ICT products and services and specifies the tasks of the European Union Agency for Network and Information Security (ENISA) in the field of cybersecurity.
In addition to the above, it is imperative to follow the International Medical Device Regulators Forum IMDRF guidelines.
EU MDR Requirements on Cybersecurity
Specific cybersecurity requirements for medical devices are mentioned in Annex I of EU MDR 2017/745. The following flowchart summarises the cybersecurity requirements mentioned in Annex I.
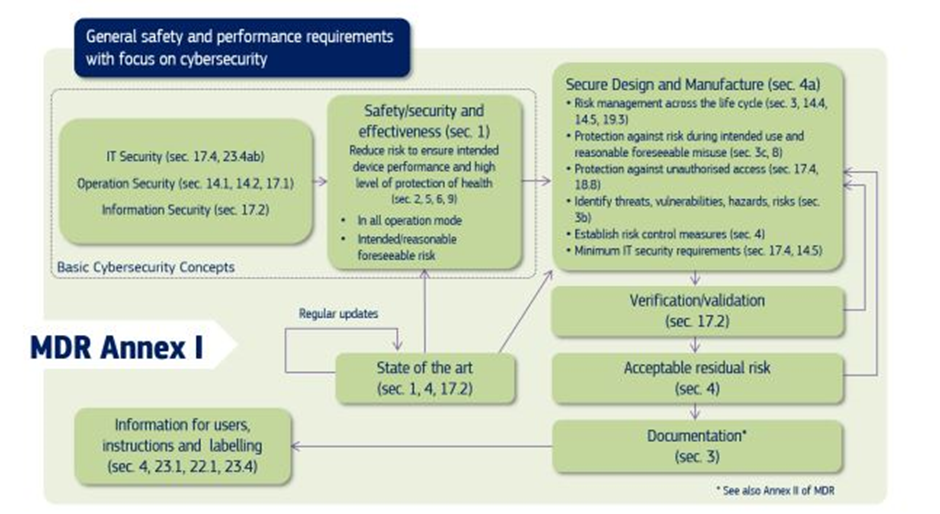
The following MDR provisions list is applicable for all medical devices. The list applies to software medical devices as well. The documentation requirement is the same for medical and software medical devices, but the document’s content varies.
- Conformity assessment procedures: Article 52
- Post-market surveillance (PMS) system, PMS plan and report: Article 83-85
- Periodic safety update report: Article 86
- Reporting of serious incidents and field safety corrective actions: Article 87
- Trend reporting: Article 88
- Analysis of serious incidents and field safety corrective actions: Article 89
- Technical documentation: Annex II and Technical documentation on post-market surveillance: Annex III
- Clinical evaluation and post-market follow-up: MDR Chapter VI and Annex XIV